Definition:
Cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) is the most widely used, evidence-based, and scientific practice for treating mental disorders. Cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) is a short-term and goal-oriented psychotherapy treatment that takes a hands-on, practical approach to problem-solving. CBT helps you become aware of inaccurate or dysfunctional thinking so you can view challenging situations in a balanced way and respond to them in a more effective way.
CBT is not about changing your thinking to a positive thinking (which is extreme) - The goal is about reaching a more Balanced way of thinking.
How CBT works:
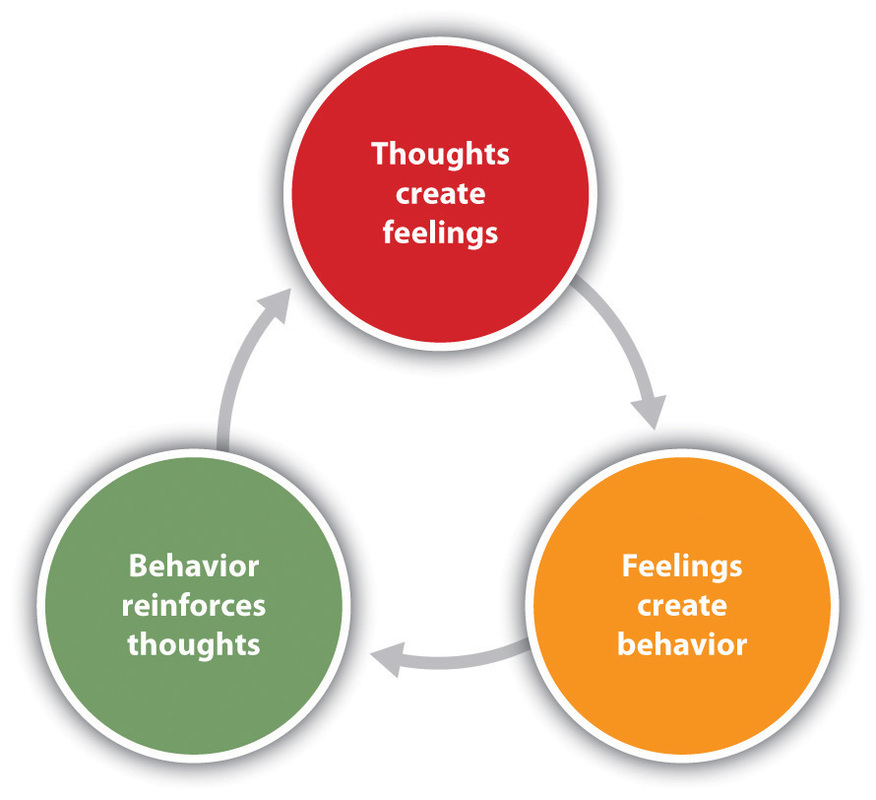
CBT is based on the concept that your thoughts, feelings, physical sensations and actions are interconnected, and that dysfunctional thoughts and behaviours can trap you in a vicious cycle.
Unlike some other talking treatments, CBT deals with your current problems, rather than focusing on issues from your past. It does touch on the past but it looks for practical ways to improve your state of mind on in the present. According to CBT, dysnfuctional beliefs are the result of childhood; however, there are behaviours and thoughts that people engage in, in the present, which maintain their current problem. By dealing with current thoughts and behaviours and changing these, a change in dysfunctional beliefs resulting from childhood will also occur in most cases.
In some cases, however, a deeper investigation of childhood might be needed.
CBT can be completed in a relatively short period of time compared to other talking therapies, and CBT teaches you useful and practical strategies that can be used in everyday life – even after the treatment has finished.
How effective is Cognitive Behavioral Therapy?
Cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) is one of the most effective treatments for psychological disorders and general stress. It can be as effective or even more effective than medication in treating some mental health problems - Once you stop taking your medications, there is a very high chance of relapse, whereas relapse rates after CBT treatment are much lower. CBT is often viewed as the psychotherapy treatment of choice for most people.
CBT can be an effective therapy for the following problems (including but not limited to):
- Anxiety Disorders (Panic Disorder, GAD, Social Anxiety including Presentation Anxiety, Phobias)
- Depression
- Drug or Alcohol Problems
- Eating Disorders
- Habits
- Bipolar Disorder
- Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder
- Health Anxiety
- Psychosis (including Schizophrenia)
- Anger Management
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder
- Trauma
- Sleep Problems
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) vs. Psychoanalysis (Freud):
| Cognitive Behavioral Therapy | Psychoanalysis (Freud) | |
| Time Frame | 2-5 months | 2 years + |
| Structure | Structured | Less Structured |
| Goals | Therapist and client set the agenda for the session based on mutually set goals. | The client, not the therapist, sets the agenda for the session by talking about whatever is on their mind. |
| Focus | Present | Past |
| Relationship with the therapist | equal power | therapist has power over client |
